Nursing Care Plan for Glaucoma
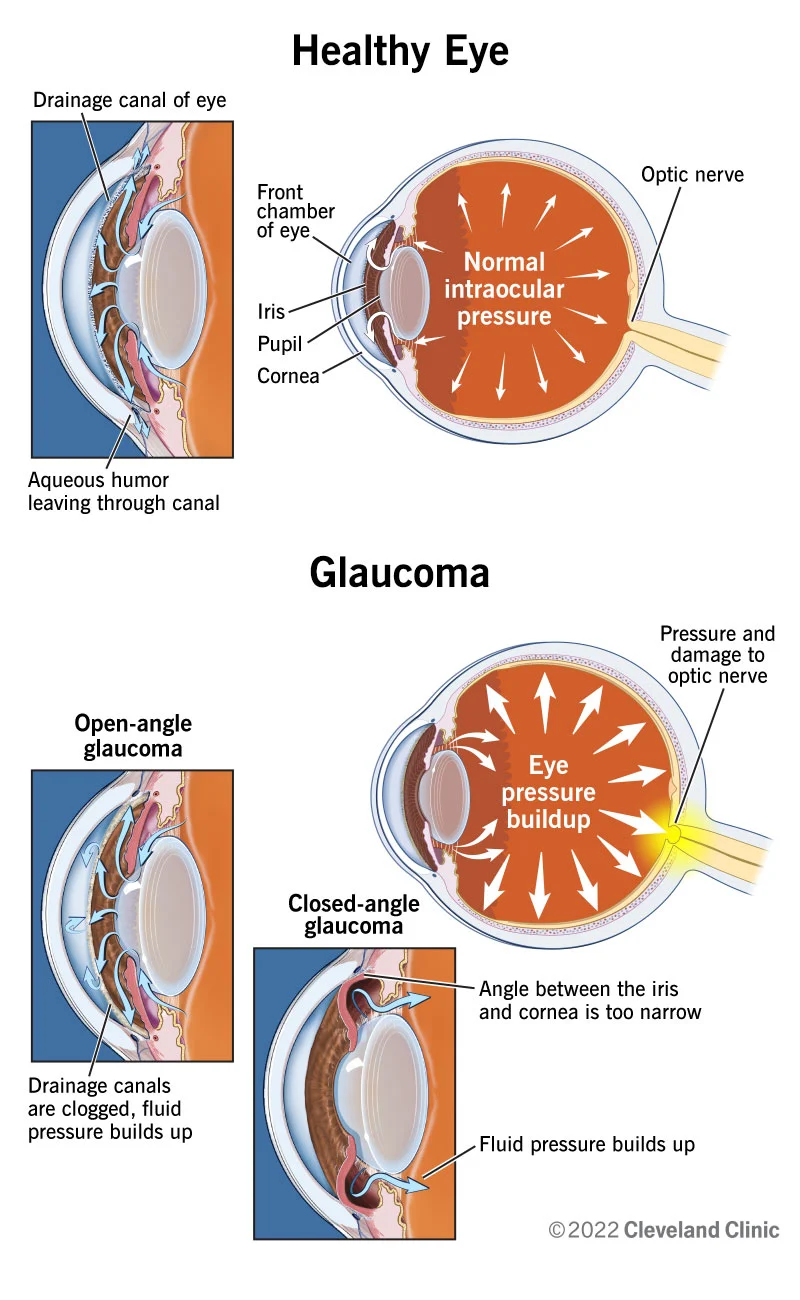
Introduction:
Glaucoma is a chronic eye condition characterized by increased intraocular pressure that can lead to optic nerve damage and vision loss. As a nurse, your role is crucial in supporting patients with glaucoma in managing their condition and preventing further vision deterioration. This nursing care plan aims to outline evidence-based interventions to assess, manage, and support patients with glaucoma.
Patient Assessment:
- Name: [Patient’s Name]
- Age: [Patient’s Age]
- Gender: [Patient’s Gender]
- Medical History: [Brief summary of patient’s medical history]
- Type of Glaucoma: [Identify the type of glaucoma, such as primary open-angle glaucoma or angle-closure glaucoma]
- Medical Diagnosis: Glaucoma
- Date of Admission: [Date of Admission]
- Date of Care Plan: [Date of Care Plan]
Subjective Data:
- Patients may report symptoms such as blurred vision, eye pain, or headache.
- Patients may express concerns about vision loss and its impact on daily activities.
Objective Data:
- Documentation of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) measured during tonometry.
- Visual field loss or changes observed during perimetry testing.
- Optic nerve damage detected during ophthalmoscopy or imaging studies.
Glaucoma Nursing Diagnosis:
- Impaired Visual Function related to increased intraocular pressure and optic nerve damage.
- Risk for Injury related to impaired peripheral vision and potential falls or accidents.
- Deficient Knowledge regarding glaucoma, treatment, and self-care measures.
- Anxiety related to the diagnosis of glaucoma and potential vision loss.
- Risk for Impaired Vision related to increased intraocular pressure and optic nerve damage as evidenced by the patient’s diagnosis of glaucoma.
- Anxiety related to potential vision loss, treatment uncertainties, and lifestyle changes is evidenced by the patient’s expressions of worry, restlessness, or fear.
- Deficient Knowledge related to glaucoma and its management as evidenced by the patient’s request for information and lack of understanding about the disease process.
Glaucoma Nursing Interventions:
Impaired Visual Function:
- Assess the patient’s visual acuity, peripheral vision, and any changes in the visual field regularly.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team to ensure appropriate medical management of intraocular pressure, such as medications, laser therapy, or surgical interventions.
- Provide education on the importance of adhering to prescribed medications and attending regular ophthalmology appointments to monitor disease progression.
- Offer emotional support and encourage the patient to express concerns and emotions related to visual changes and potential vision loss.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team to monitor and record intraocular pressure (IOP) regularly.
- Administer prescribed eye drops or medications as ordered to reduce IOP and prevent further optic nerve damage.
- Educate the patient about the importance of compliance with medication regimens and the need for regular eye examinations.
- Encourage the patient to use protective eyewear, such as sunglasses, to reduce exposure to bright sunlight or glare.
- Assist the patient in identifying and avoiding activities that may increase intraocular pressure, such as heavy lifting or straining.
Risk for Injury:
- Assess the patient’s environment for potential hazards, such as obstacles, poor lighting, or slippery surfaces.
- Educate the patient on fall prevention strategies, including keeping walkways clear, using handrails, and using appropriate lighting.
- Encourage the patient to wear protective eyewear when engaging in activities that may pose a risk to the eyes.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team to address any mobility or balance issues through physical therapy or occupational therapy referrals, if necessary.
- Assess the patient’s mobility and depth perception.
- Ensure a safe environment by removing obstacles and maintaining a clutter-free space.
- Implement fall prevention strategies, such as installing handrails or nightlights.
- Educate the patient and family about precautions to prevent eye injuries and falls.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team to consider occupational therapy consultation for home modifications if necessary.
Deficient Knowledge:
- Assess the patient’s understanding of glaucoma, its progression, and treatment options.
- Provide education on glaucoma, including its causes, risk factors, and the importance of medication adherence and regular follow-up appointments.
- Teach the patient about self-care measures, such as proper administration of eye drops, monitoring for changes in vision, and recognizing signs of complications.
- Offer written materials, reliable resources, or referrals to support groups for additional information and ongoing support.
Anxiety:
- Assess the patient’s anxiety level, coping mechanisms, and support systems.
- Provide a calm and supportive environment to help alleviate anxiety and promote relaxation.
- Offer information and reassurance about available treatment options and the importance of ongoing monitoring.
- Encourage the patient to engage in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or guided imagery.
- Establish a trusting and supportive nurse-patient relationship.
- Provide emotional support and reassurance to alleviate anxiety.
- Encourage the patient to express fears and concerns about vision loss.
- Educate the patient and family about glaucoma, its management, and available resources.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team to refer the patient to appropriate counseling or support services if needed.
Glaucoma Nursing Evaluation:
- Maintenance or improvement of visual function through appropriate medical management.
- Prevention of injuries and falls through environmental modifications and patient education.
- Increased knowledge and understanding of glaucoma, treatment options, and self-care measures.
- Reduction in anxiety levels and enhanced coping mechanisms.
- The patient’s intraocular pressure is within an acceptable range and stable.
- The patient reports a reduction in anxiety and demonstrates coping mechanisms to manage emotional distress.
- The patient expresses an understanding of glaucoma and its management, including the importance of medication compliance and regular eye examinations.
- The patient actively engages in self-care strategies and seeks appropriate support when needed.
Documentation:
Regularly document the patient’s visual assessments, medication adherence, educational interventions, and the patient’s response to treatment. Collaborate with the interdisciplinary healthcare team to review and update the care plan based on the patient’s condition and evolving needs.
Note: This nursing care plan is a general guideline and should be individualized based on the patient’s specific needs, type and stage of glaucoma, treatment plan, and healthcare provider’s recommendations.
