Congestive Heart Failure
Watch World’s Best Lecture on Heart Failure – GET FREE ACCESS FOR 7 DAYS
Heart failure often referred to as congestive heart failure is a condition when the heart is unable to pump enough blood according to the needs of the body. It is characterized as an abnormality of cardiac function (detectable or not) where the heart fails to pump blood at a rate commensurate with the requirements of the metabolizing tissues or is able to do so only with an elevated diastolic filling pressure.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS:
- Shortness of breath
- Worse with exercise
- While lying down
- May wake the person at night
- Excessive tiredness
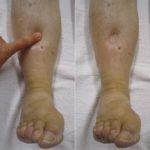
- Leg swelling
- Chest pain
- Angina
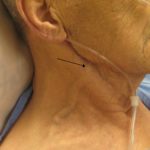
- Jugular venous distension
- Severe peripheral (pitting) edema

Causes of Congestive Heart Failure:
- Myocardial infection
- Coronary artery disease
- High blood pressure
- Atrial fibrillation
- Valvular heart disease
- Excessive alcohol use
- Cardiomyopathy
- Medications
- NSAIDS
- Anesthetic agents
- Ketamine
- Thiazolidinediones
- Cancer medications
- Salbutamol
- Tamsulosin
Diagnosis:
- A physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography
- Blood test
- Electrolytes
- Kidney function
- Liver function tests,
- Thyroid function tests
- Chest radiography or Chest X-ray
- Chest X-rays are frequently used to aid in the diagnosis of CHF. In a person who is compensated, this may show cardiomegaly (the visible enlargement of the heart), quantified as the cardiothoracic ratio (proportion of the heart size to the chest). In left ventricular failure, there may be evidence of vascular redistribution (“upper lobe blood diversion” or “cephalization”), Kerley lines, cuffing of the areas around the bronchi, and interstitial edema.
Treatment:
Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease.
Mild Chronic Heart Failure:
- Stopping smoking
- Physical exercise
- Dietary changes
Left Ventricular Heart Failure:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- Angiotensin receptor blockers
- Beta-blockers
Watch World’s Best Lecture on Heart Failure – 7 DAYS FREE TRIAL
The information provided on this website (www.MadeForMedical.com) is only for educational purpose.
While we tried hard to write quality articles but still, the articles and the information within them is not guaranteed to be free of factual errors or typos and hence may not be correct. You are advised to independently verify the claims in the articles and make your own conclusion.